-Cough and wheezing with copious sputum
and rebelious Qi, with
Tussilago farfara-
Kuan dong hua. Very common combination.
[2]
- Acute or chronic cough with blood in the sputum, with
Stemona
tuberosa- Bai bu.
[2]
- Productive cough, wheezing, and spontaneous sweating, with
Schisandra
chinensis- Wu wei zi.
[2]
- Chronic cough, especially that due to debiliating Heat, which often results
in the coughing up of blood and pus. Use with
Asparagus
cochinchinensis- Tian men dong,
Scutellaria
baicalensis- Huang qin, and
Morus alba- Sang
bai pi.
[2]
- Chronic cough due to Lung deficiency with blood streaked sputum. Use with
Anemarrhena asphodeloide- Zhi
mu and
Fritillaria cirrhosa- Chuan
bei mu.
[2]
[1] Barefoot Doctors Manual- Published
by Madrona Publishers Seattle Washington ISBN 0-914842-52-8
[2] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7
[3] Chinese Medicinal Herbs- Beatrice Bliss (1973) Compiled by Li Shi- Chen.
Translated and Researched by F. Porter Smith and G. A. Stuart. Geogetown Press,
San FranciscoISBN 0 914558005
Images
1.
en.wikipedia.org
by KENPEI CC BY-SA 3.0
2.
[1]
3.
tcm100.com Astersaponin. Shionone.[2]
Epifriedelinol, friedelin, shionone, astersaponin, quercetin, lachnophyllol,
lachnophyllol acetate, anethole, oleic acid, and aromatic acid.[1]
References
[1] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7
[2] Barefoot Doctors Manual- Published by Madrona Publishers Seattle Washington
ISBN 0-914842-52-8
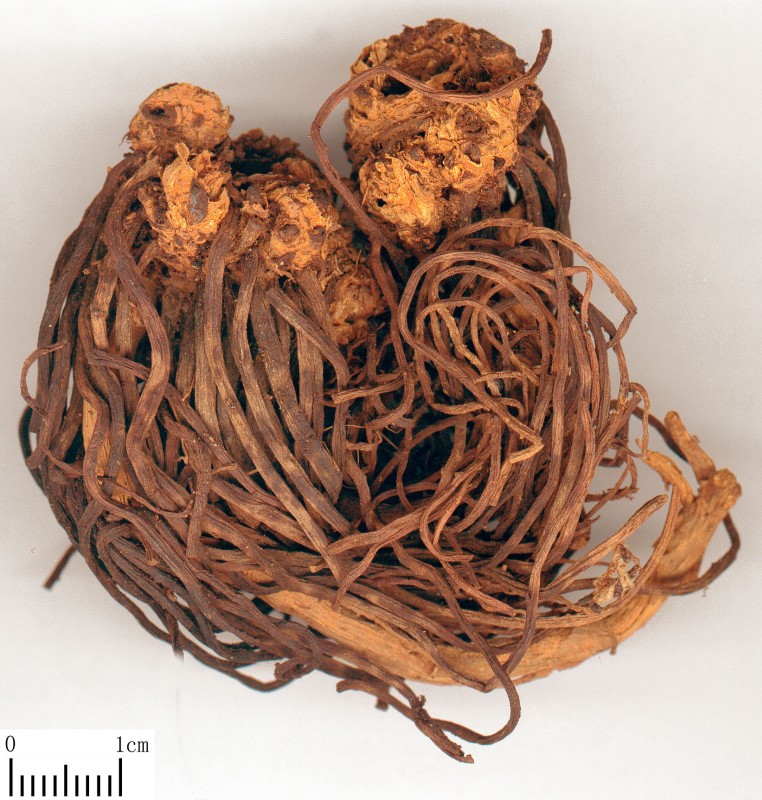
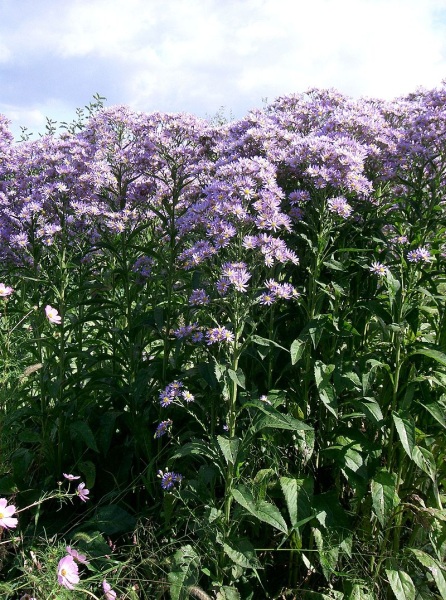 Aster
tataricus. 紫
菀 Zǐ
wǎn
Purple aster
Family: Asteraceae
Aster
tataricus. 紫
菀 Zǐ
wǎn
Purple aster
Family: Asteraceae