[1] Barefoot Doctor's Manual- 1977 Prepared by the Revolutionary Health Committee
of Hunan Province. Original Chinese manual- Victor W. Sidel. Originally published
by Dr Joseph Quin and the Fogarty International centre, Bethdesda (1974). Madrona
Publishers Seattle Washington ISBN 0-914842-52-8
[2] A Complete English Dictionary of Medicinal Terms in Chinese Acupuncture and
Herbalism 1981- Henry Lu Chinese Foundations of Natural Health- The Academy of
Oriental Heritage, Vancouver, Canada.
[3] Translation notes from Gary Seiford and Hocu Huhn- NSW College of Natural
Therapies. Sydney Australia.
Images
1.
en.wikipedia.org
by Vinayaraj CC BY-SA 3.0
2.
[1]
3.
plumdragonherbs.com HABITAT:
HABITAT: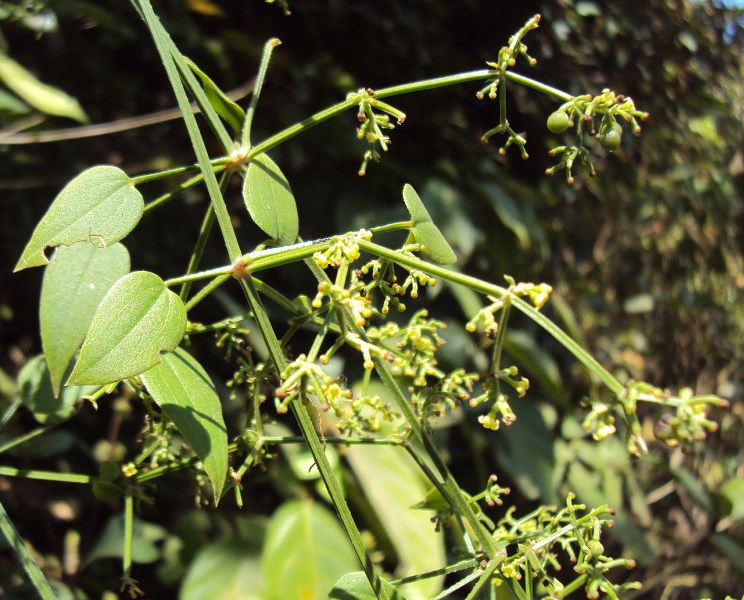

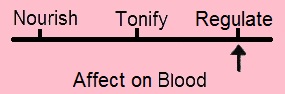 FLAVOR: Bitter CHANNELS:
Liver
FLAVOR: Bitter CHANNELS:
Liver
 HABITAT:
Grows wild under cover of damp wet upland forests.
HABITAT:
Grows wild under cover of damp wet upland forests.