Antihypertensive agent (it dilates blood
vessels).[4]
[1] Barefoot Doctor's Manual- 1977 Prepared by the Revolutionary Health Committee
of Hunan Province. Original Chinese manual- Victor W. Sidel. Originally published
by Dr Joseph Quin and the Fogarty International centre, Bethdesda (1974). Madrona
Publishers Seattle Washington ISBN 0-914842-52-8
[2] A Complete English Dictionary of Medicinal Terms in Chinese Acupuncture
and Herbalism 1981- Henry Lu Chinese Foundations of Natural Health- The Academy
of Oriental Heritage, Vancouver, Canada.
[3] Medicated Diet of Traditional Chinese Medicine- Chief Editor- Hou Jinglun.
Associate Editors- Zhao Xin, Li Weidong, Liu Jianxin, Geng Chun-e, Li Guohua,
Li Shaohua. Geijing. Science & Technology Press 1994. ISBN 7-5304-1735-5/R.
309.
[4] Translation notes from Gary Seiford and Hocu Huhn- NSW College of Natural
Therapies. Sydney Australia (1982).
[5] Chinese System of Food Cures Prevention and Remedies. 1986
Lu,
Henry. Sterling Publishing Co., Inc. New York. USA. Distributed in Australia
by Capricorn Book Co. Pty Ltd. Lane Cove, NSW. ISBN 0-8069-6308-5.
[6] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7
Images
1.
www.ecosystem.ru
2.
tcmwiki.com
3.
tcmwiki.com
4.
en.wikipedia.org
by Fukutaro GFDL
5.
en.wikipedia.org
by Kloisiie CC BY-SA 3.0
6.
en.wikipedia.org
by Kloisiie Public Domain
7.
en.people.cn
8.
en.wikipedia.org
by Flickr upload bot CC BY-SA 2.0
9.
commons.wikimedia.org
by Derek Ramsey CC SA 3.0 Unported
10.
uknow01.com Nelumbo
nucifera. 莲
Lián Lotus
Family: Nymphaeaceae
Nelumbo
nucifera. 莲
Lián Lotus
Family: Nymphaeaceae
 FLAVOR: Sweet, astringent, pleasant,
acrid CHANNEL: Spleen, Kidney, Heart
FLAVOR: Sweet, astringent, pleasant,
acrid CHANNEL: Spleen, Kidney, Heart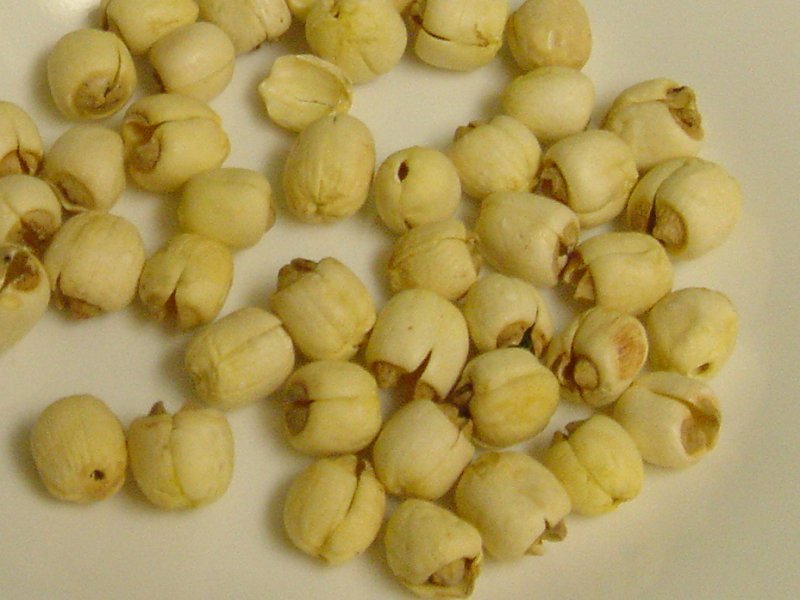
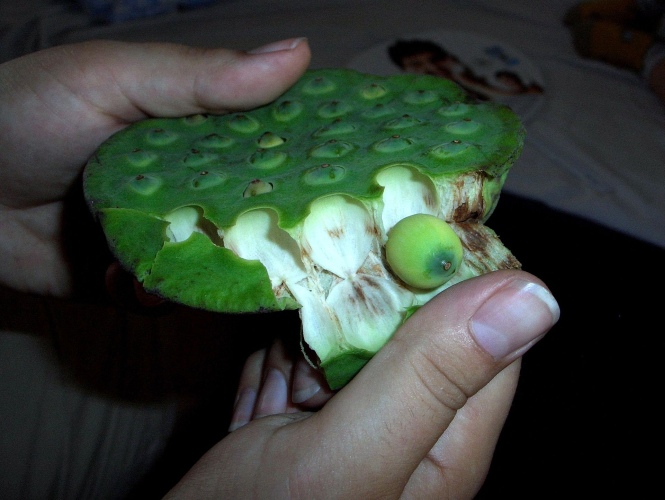 - Relieve discharge of a short stream of red urine- Mix 180 g lotus seeds and
30 g licorice and grind into powder. Take 3-6 g powder each time with warm water,
3 times a day.[5]
- Relieve discharge of a short stream of red urine- Mix 180 g lotus seeds and
30 g licorice and grind into powder. Take 3-6 g powder each time with warm water,
3 times a day.[5]
 莲
子 心
Lián zǐ xīn Plumule-
Green bud of a ripe dry lotus seed-
Harvested in Autumn
莲
子 心
Lián zǐ xīn Plumule-
Green bud of a ripe dry lotus seed-
Harvested in Autumn
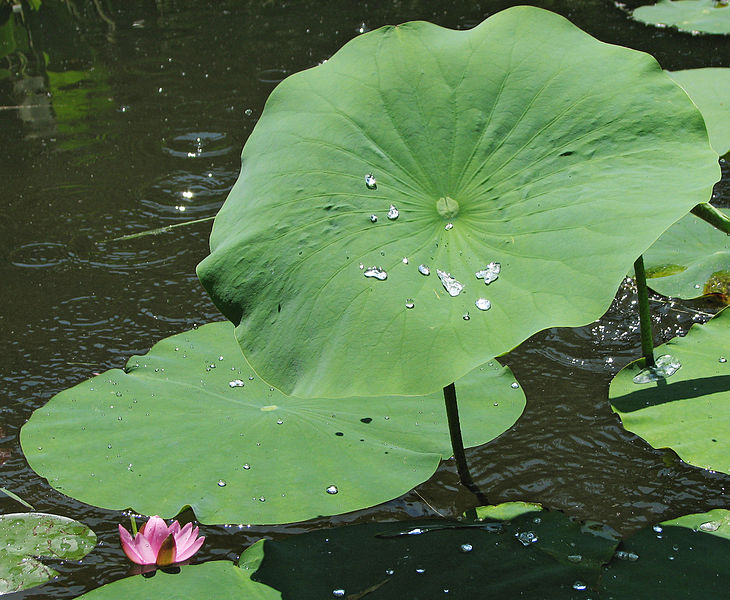 荷
叶 Hé
yè Lotus leaf, Fresh or dry leaf-
harvested in Summer
荷
叶 Hé
yè Lotus leaf, Fresh or dry leaf-
harvested in Summer

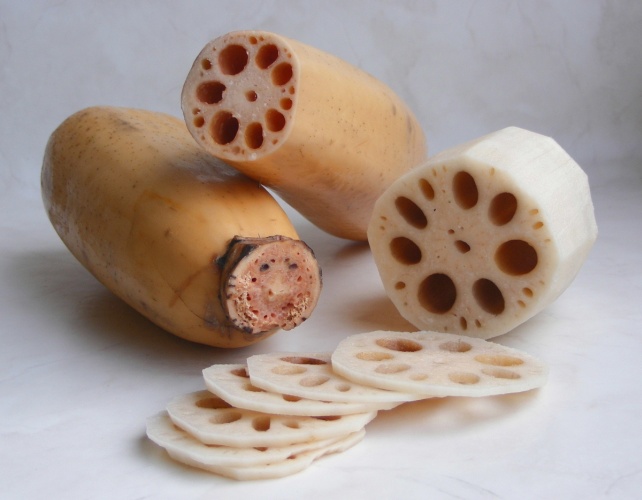
 藕
节 Ŏu
jíe, Lian geng
Lotus stem and root, Rhizome
藕
节 Ŏu
jíe, Lian geng
Lotus stem and root, Rhizome
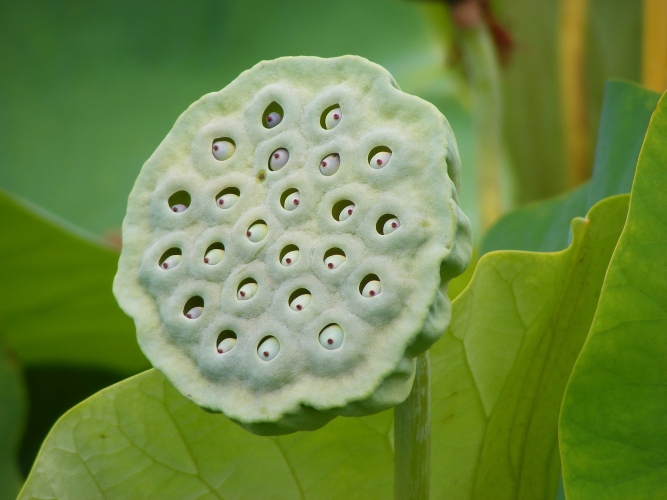
 莲
房
Lián fáng Mature Lotus floral receptacle,
Lotus fruit, Lotus seed pot
莲
房
Lián fáng Mature Lotus floral receptacle,
Lotus fruit, Lotus seed pot
