- Ascites, with
Euphorbia
kansui- Gan sui.
[3]
- Edema and abdominal distention due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and Kidney,
with
Aquilaria sinensis- Chen xiang and
Cinnamomum cassia- Rou gui.
[3]
- Constipation, with
Prunus persica-
Tao ren. Both ingredients are ground into powder and made into pills with the
addition of honey.
[3]
- Wheezing, a sensation of fullness in the chest, edema, and abdominal distention
due to obstruction of the Lung Qi by congested fluids. Use with
Lepidium
apetalum- Ting li zi and
Prunus
armeniaca- Xing ren.
[3]
- Abdominal pain and constipation due to intestinal parasites, with
Bing
lang.
[3]
[1] Barefoot Doctor's Manual- 1977 Prepared by the Revolutionary Health Committee
of Hunan Province. Original Chinese manual- Victor W. Sidel. Originally published
by Dr Joseph Quin and the Fogarty International centre, Bethdesda (1974). Madrona
Publishers Seattle Washington ISBN 0-914842-52-8
[2] A Complete English Dictionary of Medicinal Terms in Chinese Acupuncture
and Herbalism 1981- Henry Lu Chinese Foundations of Natural Health- The Academy
of Oriental Heritage, Vancouver, Canada.
[3] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7
[4]
sacredlotus.com
[5] Translation notes from Gary Seiford and Hocu Huhn- NSW College of Natural
Therapies. Sydney Australia.
Images
1.
wikipedia.org
by KENPEI CC BY-SA 3.0
2.
[1]
3.
tcm100.com
4.
tcmwiki.com
Pharbitin; includes phabitic acid and ipurolic acid, nilic acid, gallic acid,
lysergol, chanoclavine, penniclavine, isopenniclavine, elymoclavine.[1]
References
[1] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7
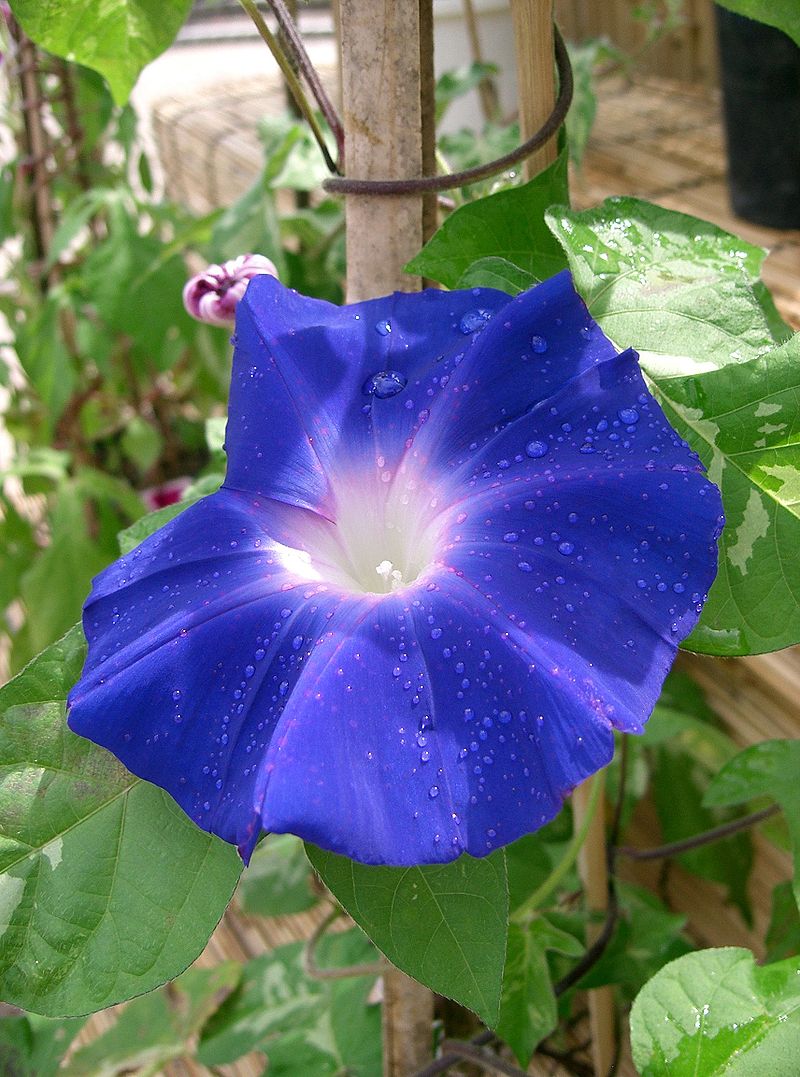 Ipomoea
nil. Ipomoea hederaceae, Pharbitis nil
牽 牛
子
Qiān niú zǐ Morning
glory flower Family: Convolvulaceae
Ipomoea
nil. Ipomoea hederaceae, Pharbitis nil
牽 牛
子
Qiān niú zǐ Morning
glory flower Family: Convolvulaceae