- Scanty urine and edema due to obstruction
by dampness, with
Dong gua pi. For
fever with scanty, dark urine due to Dampness obstructing the channels, use
with
Vigna umbellata- Chi xiao dou and
Talcum-
Hua shi, and
Akebia trifoliata- Mu tong.
[6]
- Diarrhea due to Spleen deficiency, with
Poria
cocos- Fu ling and
Atractylodes
macrocephala- Bai zhu.
[6]
- Lung abscess, with
Phragmites communis-
Lu gen,
Benincasa hispida- Dong gua ren,
and
Prunus persica- Tao ren.
[6]
- Intestinal abscess, with
Patrinia scabiosifolia-
Bai jiang cao and
Paeonia suffruticosa-
Mu dan pi.
[6]
- Early stage Intestinal abscess due to Dampness and Blood stasis. Use with
Trichosanthes kirilowii- Gua lou
ren and
Prunus persica- Tao ren.
[6]
- Wind Dampness induced generalized body aches. Use with
Ephedra
sinica- Ma huang,
Prunus armeniaca-
Xing ren and
Glycyrrhiza uralensis-
Gan cao.
[6] [1] Barefoot Doctor's Manual- 1977 Prepared
by the Revolutionary Health Committee of Hunan Province. Original Chinese manual-
Victor W. Sidel. Originally published by Dr Joseph Quin and the Fogarty International
centre, Bethdesda (1974). Madrona Publishers Seattle Washington ISBN 0-914842-52-8
[2] Chinese System of Food Cures Prevention and Remedies. 1986 Lu, Henry. Sterling
Publishing Co., Inc. New York. USA. Distributed in Australia by Capricorn Book
Co. Pty Ltd. Lane Cove, NSW. ISBN 0-8069-6308-5.
[3] Medicated Diet of Traditional Chinese Medicine- Chief Editor- Hou Jinglun.
Associate Editors- Zhao Xin, Li Weidong, Liu Jianxin, Geng Chun-e, Li Guohua,
Li Shaohua. Geijing. Science & Technology Press 1994. ISBN 7-5304-1735-5/R.
309.
[4] Chinese System of Food Cures Prevention and Remedies. 1986
Lu,
Henry. Sterling Publishing Co., Inc. New York. USA. Distributed in Australia by
Capricorn Book Co. Pty Ltd. Lane Cove, NSW. ISBN 0-8069-6308-5.
[5] Translation notes from Gary Seiford and Hocu Huhn- NSW College of Natural
Therapies. Sydney Australia (1982).
[6] Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica- Dan Bensky and Andrew Gamble- Eastland
Press 1986 Seattle Washington ISBN 0-939616-15-7.
Images
1.
en.wikipedia.org by
Jed CC BY-SA 3.0
2.
[2]
3.
vitaminsupplementingredients.com
4.
shimaneorganicfarm.com
 Coix lachryma. 薏
苡 仁
Yì yǐ rén Job's
tears seeds, Pearl
Barley, Adlay
Family: Gramineace
Coix lachryma. 薏
苡 仁
Yì yǐ rén Job's
tears seeds, Pearl
Barley, Adlay
Family: Gramineace


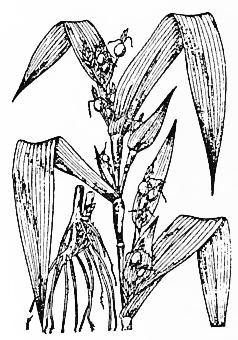 HABITAT:
Grows wild or cultivated.
HABITAT:
Grows wild or cultivated.