Gall Bladder Channel
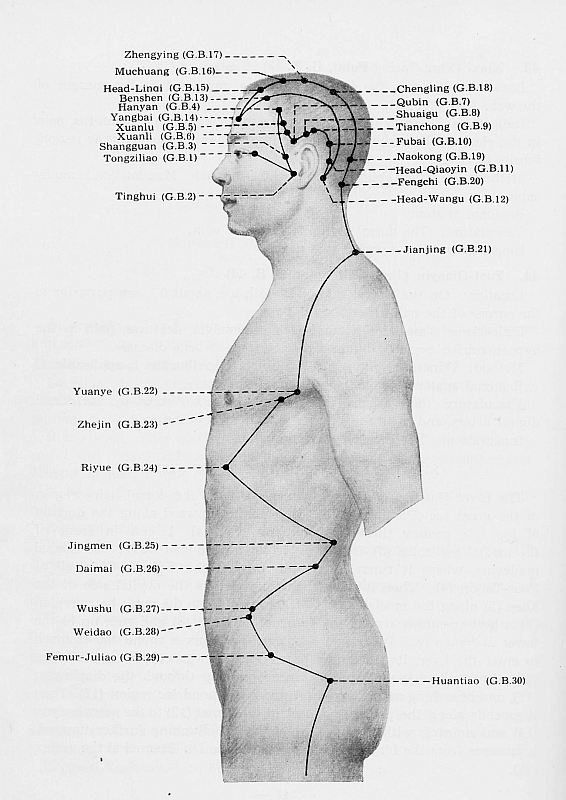
Gall Bladder Channel

The most lateral channel, known for causing one sided symptoms, such as hip pain and migraines.
GB 1 Tongziliao **
FUNCTIONS: Eliminate Wind-Heat, dispel Fire, and brighten the eyes.
1. Opthalmalgia.[1] Failing of vision.[1]
Redness of the eye and lacrimation.[1]
Keratitis.[2] Ametropia.[2]
Night blindness.[2] Atrophy of the
optic nerve.[2]
2. Headache.[1,2]
LOCATION: Lateral to the outer canthus, in the depression on the
lateral side of the orbit.[1]
METHOD: Laterally 3-8 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 2 Tinghui **
FUNCTIONS: Clear Jingluo, soothe the ears, eliminate Wind.
INDICATIONS
1. Tinnitus.[1,2] Deafness.[1,2]
Toothache.[1,2]
2. Otitis media.[2] Deaf mutism.[2]
3. Facial paralysis.[2]
LOCATION: Anterior to the intertragic notch, directly below Tinggong-
SI19, at the posterior border of the condyloid process of the mandible. The
point is located with the mouth open.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicularly 13-18 mm.[1]
GB 3 Shangguan*
INDICATIONS
1. Deafness.[1,2] Tinnitus.[1,2]
Toothache.[1,2] Otitis media.[2]
2. Facial paralysis.[1,2] Headache.[1]
Lockjaw.[2]
LOCATION: In front of the ear, on the upper border of the zygomatic
arch, in the depression directly above Xiaguan- St7.[1]
METHOD: Perp 8 mm. Deep puncture is not advisable.[1]
GB 4 Hanyan *
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[1,2] Pain in the
outer canthus.[1] One-sided headache.[1]
2. Tinnitus.[1,2]
3. Seizures. Convulsions.[2]
4. Blurring of vision.[1]
5. Rhinitis.[2]
LOCATION: Within the hairline of the temporal region, midway
of the upper half of the distance between Touwei- St 8 and Qubin- GB 7.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle
directed posteriorly.[1]
GB 5 Xuanlu*
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[1,2] Pain in the
outer canthus.[1] One-sided
headache.[1]
2. Facial swelling.[2]
3. Toothache.[2]
4. Neurasthenia[2]
LOCATION: Within the hairline of the temporal region, midway of the border
line connecting Touwei (St8) and Qubin (GB7).[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
 GB
6 Xuanli*
GB
6 Xuanli*
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine headache.[1,2]
Pain in the outer canthus.[1] One-sided
headache.[1]
2. Facial swellng.[2]
3. Toothache.[2]
2. Neurasthenia.[2]
LOCATION: Within the hairline inferior to the corner of the temporal
region, midway between Xuanlu- GB5 and Qubin- GB7.[1]
METHOD: 5-8 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 7 Qubin*
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the temporal region.[1]
Lockjaw.[1] Migraine headache.[2]
Trigeminal neuralgia.[2] Spasms of
temporalis muscle.[2]
2. Swelling of the cheek and submandibular region.[1]
LOCATION: Within the hairline anterior and superior to the auricle,
about 1 finger breadth anterior to Jiaosun- SJ 20.[1]
METHOD: 5-8 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 8 Shuaigu*
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[1,2]One-sided
headache.[1]
2. Vertigo.[2]
3. Eye diseases.[2]
LOCATION: Superior to the apex of the auricle, 1.5 cun within the
hairline.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 9 Tianchong *
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1,2]
2. Mental disturbance of depressive type.[1]
Seizures.[2]
3. Swelling of the gums.[1] Gingivitis.[2]
4. Goiter.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior and superior to the auricle, 2 cun within
the hairline, about .5 cun posterior to Shuaigu- GB8.[1]
METHOD:8 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 10 Fubai*
INDICATIONS
1. Tinnitus.[1,2] Deafness.[1,2]
2. Headache.[1]
3. Toothache.[2]
4. Bronchitis.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior and superior to the mostoid process, in the
middle of the
curve line drawn from Tianchong- GB9 to head-Qiaoyin- GB11.[1]
METHOD: 8 mm lorizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 11 Head - Qiaoyin*
INDICATIONS
1. Earache.[1,2]
Deafness.[1,2] Tinnitus.[1,2]
2. Headache.[1,2] Pain
in the neck.[1] Stiff neck.[2]
3. Bronchitis.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior and superior to the mastoid process, on the line
connecting Fubai- GB10, and Head-Wangu GB12.[1]
METHOD: 8 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 12 Head - Wangu*
FUNCTIONS: Eliminate Wind. Insomnia.
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1] Facial paralysis.[1,2]
Pain and stiffness of the neck.[1]
2. Facial swelling.[1,2] Toothache.[1,2]
3. Seizures.[1,2]
4. Insomnia.[1]
5. Parotitis.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression posterior and inferior to the mastoid process.
In angle formed by the posterior edge of mastoid process and inferior edge of
occipid.[1,2]
METHOD: Obliquely downward 8-13 mm inch.[1]
GB 13 Benshen *
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1,2] Stiff neck.[2]
Costalgia.[2] Hemiplegia.[2]
2. Seizures.[1,2] Vertigo.[2]
3. Blurring of vision.[1]
LOCATION: 0.5 cun within the hairline of the forehead, at the junction
of the medial 2/3rds and lateral 1/3rd of the distance from Shenting- Du24 to
Touwei- St8. In line with lateral corner of eye.[1,2]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 14 Yangbai**

FUNCTIONS: Dispel Wind, brighten the eyes, stop pain. Much used in
migraine and facial paralysis.
INDICATIONS
1. Blurring of vision.[1] Lacrimation
on exposure to wind.[1] Pain in the
outer canthus.[1] Twitching of eyelids.[1]
Supraorbital neuralgia.[2] Ptosis.[2]
Eye diseases.[2]
2. Frontal headache.[1] Facial paralysis.[2]
LOCATION: On the forehead, 1 cun above the midpoint of the eyebrow, approximately
at the junction of the upper 2/3rds and lower 1/3rd of the vertical line drawn
from the anterior hairline to the eyebrow.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
downward.[1]
GB 15 Head - Linqi*
INDICATIONS
1. Blurring of vision.[1] Lacrimation
on exposure to wind.[1] Pain in the
outer canthus.[1] Pannus.[2]
Acute and chronic conjunctivitis.[2]
2. Nasal obstruction.[1,2]
3. Vertigo.[2] Apoplectic coma.[2]
Seizures.[2]
4. Headache.[1]
5. Malaria.[2]
LOCATION: Directly above Yangbai- GB14, 0.5 cun within the hairline,
midway between Shenting- Du 24 and Touwei- St8.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
upward.[1]
GB 16 Muchuang*
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1]
2. Blurring of vision.[1] Red and
painful eyes.[1] Conjunctivitis.[2]
3. Vertigo.[2] Apoplectic coma.[2]
4. Facial edema.[2]
5. Toothache.[2]
LOCATION: 1.5 cun posterior to Head-Linqi- GB15, on the line connecting
Head-Linqi- GB15 and Fengchi- GB20.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally aong the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 17 Zhengying *
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[2] Headache[2]
Stiff neck.[2] One-sided headache.[1]
2. Vertigo.[2]
3. Vomiting.[2]
4. Blurring of vision.[1]
5. Toothache.[2]
LOCATION: 1.5 cun posterior to Muchuang- GB16, on the line joining Head-
Lingqi- GB15 and Fengchi- GB20.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 18 Chengling*
INDICATIONS
1. Epistaxis.[1,2] Rhinorrhea.[1]
Common cold.[2] Bronchitis.[2]
Occluded nose.[2]
2. Headache.[1,2]
3. Eye diseases.[2]
LOCATION: 1.5 cun posterior to Zhingying- GB17, on the line connecting
Head-Lingqi- GB15 and Fenchi- GB20. 5 cun from anterior hair line.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin with the needle directed
posteriorly.[1]
GB 19 Naokong*
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1,2] Pain and
stiffness of the neck.[1]
2. Seizures.[2] Mental illness.[2]
3. Common cold.[2] Asthma[2]
Tinnitus.[2]
4 Palpitations.[2]
LOCATION: Directly above Fengchi- GB20, level with Naohu- Du17,
on the lateral side of the external occipital protuberance. 1.5 cun up from
GB 20.[1,2]
METHOD: Downward 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
GB 20 Fenchi**

FUNCTIONS: Soothe the Liver and pacify the Yang. Clears the mind,
benefits hearing and vision, eliminate Wind and relieve Heat. Very much used
to eliminate Wind.
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1,2] Pain
and stiffness of the neck.[1,2] Pain
in the shoulder and back.[1]
Hemiplegia.Dizziness.[1]
2. Rhinorrhea.[1,2] Common
cold.[1,2] Tinnitus.[2]
Deafness.[2]
3. Vertigo.[2] Seizures.[2]
Brain diseases.[2]
4. Red and painful eyes.[1]
5. Eye diseases.[2]
6. Hypertension.[2]
7. Febrile diseases.[1]
LOCATION: In the posterior aspect of the neck, below the occipital
bone, in the depression between the upper portion of the sternocleidomastoideus
and the trapezius.[1]
METHOD: 13-25 mm towards the tip of the nose.[1]
GB 21 Jianjing**
INDICATIONS
1. Neck rigidity.[1] Pain in the shoulder
and back.[1] Motor impairment of the
hand and arm.[1] Apoplexy.[1]
Hemiplegia due to stroke.[2] Pain
in the back of the shoulder.[2]
2. Mastitis.[1,2] Difficult
labour.[1] Functional uterine bleeding.[2]
3. Scrofula.[2]
NOTE Don't use this point in pregnancy- action on uterus and breast.
LOCATION: Midway between Dazhui- Du14 and the acromion, at the highest
point of the shoulder.[1]
METHOD: Puncture perpendicularly 12mm.[1]
GB22 Yuanye*
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the hypochondriac region.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Pain of
the shoulders and arm.[2]
2. Swelling of the axillary region.[1]
Axillary lymphadenitis.[2]
3. Pleurisy.[2]
LOCATION: On the midaxillary line, 3 cun below the axilla.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 23 Zhejin *
INDICATIONS
1. Asthma.[1,2] Pleurisy.[2]
2. Vomiting.[2] Acidic belching.[2]
3. Fullness of the chest.[1]
LOCATION: 1 cun anterior to Yuanye- GB22, approximately level with the
nipple.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 24 Riyu*

FUNCTIONS: Eliminate Damp-Heat. Much used in cholecystitis.
INDICATIONS
1. Jaundice.[1] Cholecystitis.[2]
Acute and chronic hepatitis.[2]
2. Hiccup.[1,2] Intercostal
neuralgia.[2]
3. Vomiting.[1] Regurgitation.[1]
Peptic ulcer.[2]
LOCATION: Inferior to the nipple, between the cartilages of the 7th and
8th ribs, one rib below Qimen- Liv14.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 25 Jingmen *
INDICATIONS
1. Borborygmus.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
Abdominal distension.[1] Intestinal
hernia.[2]
2. Pain in the lower back and hypochondriac region.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Lumbago[2]
3. Nephritis.[2]
LOCATION: On the lateral side of the abdomen, on the lower border of
the free end of the 12th rib.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 26 Daimai**

FUNCTIONS: Regulates the Girdle channel, and alleviates Damp-Heat.
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1,2]
Leukorrhea.[1] Endometriosis.[2]
Cystitis.[2] Profuse menstruation
and leukorrhea.[2]
2. Pain in the lower back and hypochondriac region.[1]
Paraplegia due to trauma.[2] Hernia.[1]
LOCATION: Directly below the free end of the 11th rib (Zhangmen- Liv13),
level with the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
GB 27 Wushu**
INDICATIONS
1. Leukorrhea.[1,2] Endometritis.[2]
Orchitis.[2]
2. Low back pain.[1,2] Hip
joint pain.[2]
3. Hernia.[1,2]
LOCATION: In the lateral side of the abdomen, in front (medial) of the
anterior superior iliac spine, 3 cun below the level of the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
GB 28 Weidao*
INDICATIONS
1. Prolapse of uterus.[1,2]
Leukorrhea.[1] Endometritis.[2]
2. Lower abdominal pain.[1]Intestinal
hernia.[2] Chronic constipation.[2]
3. Pain in the lower back and hip joint.[1]
4. Adenitis.[2]
LOCATION: Anterior and inferior to the anterior superior iliac
spine, .5 cun anterior and inferior to Wushu- GB27.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
GB 29 Femur-Juliao**
1. Pain in the back and leg.[1,2]
Paralysis.[1] Lower abdominal
pain.[2] Disease of the hip joint
and surrounding soft tissues.[2]
2. Orchitis.[2] Endometritis.[2]
Cystitis.[2]
3. Stomache ache.[2]
LOCATION: Midway between the anterosuperior iliac spine and the great
trochanter. Locate this point in lateral recumbent position.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
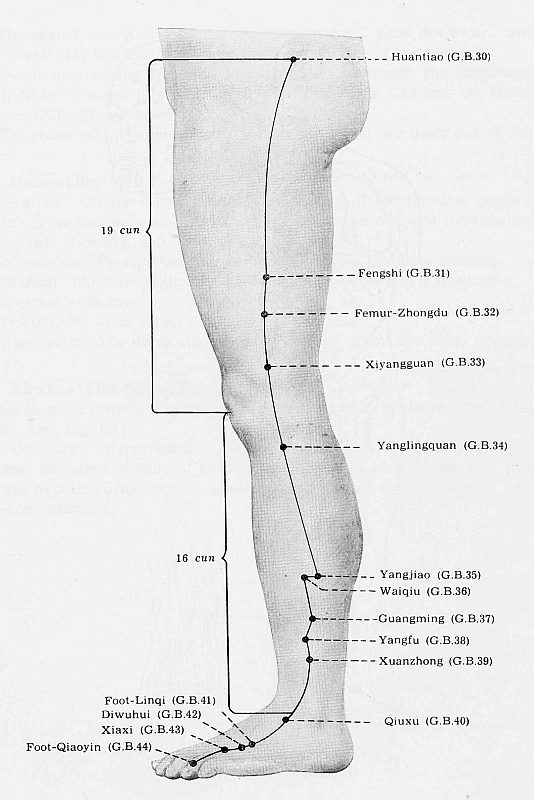
GB 30 Huantiao**

FUNCTIONS: Activate and clear Jingluo, tonify lower back-waist and
knee joints. Very much used for sciatica.
1. Pain in the lower back.[1,2]
Pain and weakness/numbness of hip and leg.[1,2]
Muscular atrophy.[1] Motor impairment.[1]
Hemiplegia.[1] Sciatica.[2]
LOCATION: At the junction of the middle and lateral third of the
distance between the great trochanter and the hiatus of the sacrum (Yaoshu Du2).
when locating the point, put the patient in lateral recumbent position with
the thigh flexed.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 38-63 mm.[1]
GB 31 Fengshi **

FUNCTIONS: Dispel Wind, relax tendons, clear Jingluo, tonify waist
knees. Much used to dispel Wind in herpes zoster and Wind-stroke.
INDICATIONS
1. Hemiplegia.[1] Muscular atrophy.[1]
Impairment and pain of the lower extremities.[1]
Paralysis of lower limb.[2] Pain in
lower back and leg.[2] Neuritis of
the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh and a muscle branch of the femoral
nerve.[2]
2. Pruritus.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the lateral aspect of the thigh, 7
cun above the transverse popliteal crease. When the patient is standing erect
with the hands close to the sides, the point is where the tip of the middle
finger touches.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 18-30 mm.[1]
GB 32 Femur-Zhongdu *
INDICATIONS
1. Muscular atrophy.[1] Motor impairment.[1]Numbness
and pain and weakness of the lower extremities.[1]
Hemiplegia.[1] Paralysis of leg.[2]
Sciatica.[2]
2. Beriberi.[2]
LOCATION: In the lateral aspect of the thigh, 5 cun above the transverse
popliteal crease, between vastus lateralis and biceps femoris.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
GB 33 Xiyangguan**
1. Pain and swelling of the knee.[1,2]
Contracture of the tendons in popiteal fossa.[1]
Numbness of the leg.[1] Paralysis
of leg.[2]
LOCATION: When the knee is flexed, the point is 3 cun above Yanglinguan-
GB34, lateral to the knee joint, in the depression between the tendon of biceps
femoris and the femur.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13 mm.[1]
GB 34 Yanglingquan**

FUNCTIONS: Benefits Liver and GB, clears and cools Damp-Heat,
clear Jingluo, activate Jingluo, strengthen tendons and bones. Eliminates Phlegm-fire
in Stomach. Very much used to subdue Liver Yang. Milder than Taichong.
INDICATIONS
1. Numbness/paralysis of the leg.[1,2]
Pain and swelling of the knee.[1,2]
Hemiplegia.[1] Muscular atrophy.[1]Motor
impairment.[1]Pain in the hypochondriac
and costal region.[1] Intercostal
neuralgia.[2] Perifocal inflammation
of the shoulder.[2]
2. Hepatitis.[2] Cholecysitis.[2]
Round worm in the bile duct.[2] Bitter
taste in mouth.[1]
3. Vomiting.[1] Habitual constipation.[2]
4. Hypertension.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression anterior and inferior to the head of the
fibula.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm.[1]
GB 35 Yangjiao *
INDICATIONS
1. Knee pain.[1]Muscular atrophy and
weakness of the foot.[1]Pain on lateral
aspect of leg.[2] Sciatica[2]
2. Fullness of hypochondriac region.[1]
3. Fullness of chest.[1]
4. Asthma.[2]
LOCATION: 7 cun above the tip of the external malleolus, on the posterior
border of the fibula, with the distance between the tip of the external malleolus
and Yanglingquan- GB34, level with Waiqiu- GB36 and Feiyang- UB58.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
GB 36 Waiqiu*
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the neck, chest and hypochondriac region.[1]Headache.[2]
Paralysis of leg.[2]
2. Hepatitis.[2]
LOCATION: 7 cun above the tip of the external malleolus, on the anterior
border of the fibula.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
GB 37 Guangming **
FUNCTIONS: Regulates the Liver, clears the vision.
INDICATIONS
1. Night blindness.[1,2] Opthalmalgia.[1]
Atrophy of the optic nerve.[2] Cataract.[2]
2. Pain in the knee.[1]Muscular atrophy.[1]Motor
impairment and pain of the lower extremities.[1]
Pain along lateral aspect of calf.[2]
3. Migraine.[2]
4. Distending pain of the breast.[1]
LOCATION: 5 cun directly above the tip of the external malleolus, on
the anterior border of the fibula.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 18-25 mm.[1]
GB 38 Yangfu*
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[1,2] One-sided
headache.[1] Pain in the outer canthus,
supraclavicular fossa and axillary region.[1]
Pain in the chest, hypochondriac region and lateral aspect of the lower extremities.[1]
Hemiplegia.[2] Paralysis of
lower limb.[2] Arthritis of knee.[2]
2. Scrofula.[1,2]
3. Malaria.[1]
LOCATION: 4 cun above and slightly anterior to the tip of the external
malleolus, on the anterior border of the fibula, between extensor digitorum
longus and peroneus brevis.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-18 mm.[1]
GB 39 Xuanzhong**
FUNCTIONS: Dispel Wind and Damp, tonify bone marrow. Treat Wei and
Bi syndromes.
INDICATIONS
1. Hemiplegia.[1,2]
Stiff neck.[1,2] Pain
in the knee and leg.[1] Migraine.[2]
Sciatica.[2] Diseases of the knee
and ankle joints and surrounding soft tissues.[2]
Distension of the abdomen.[1]
2. Fullness of the chest.[1]Pain in
the hypochondriac region.[1]
3. Beriberi.[1]
4. Scrofula.[2]
LOCATION: 3 cun above the tip of the external malleolus, in the deression
between the anterior border of the fibula and the tendons of peroneus longus
and brevis.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 10-13 mm.[1]
GB 40 Qiuxu**

FUNCTIONS: Spreads Liv Qi and benefits GB (Zulingqi GB41 better for
internal organs)
Invigorate Jingluo, ease joints. For after effects of Wind-stroke, infantile
paralysis, Wei syndrome.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the neck, chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
Muscular atrophy.[1] Motor impairment.[1]
Weakness and pain of the lower extremities.[1]
Pain and swelling in the lateral aspect of the ankle joint.[1]
Pain in the chest and ribs.[2] Sciatica.[2]
Diseases of the ankle and surrounding soft tissues.[2]
2. Swelling of the axillary lymph nodes.[1,2]
3. Vomiting.[1] Acid regurgitation.[1]
4. Cholecystitis.[2]
5. Malaria.[1]
LOCATION: Anterior and inferior to the external malleolus, in the depression
on the lateral side of the tendon of extensor digitorum longus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 41 Foot-Linqi**
FUNCTIONS: Spreads and drains Liv and GB, to dispel Damp-Heat. For
hypochondrium (higher than Li). Clears and regulates the girdle channel.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the outer canthus.[1] Pain
in the costal and hupochondriac region.[1]Pain
and swelling of the dorsum of foot.[1]
Headache.[2] Rib pain.[2]
2. Distending pain of the breast.[1]
Mastitis.[2] Abscesses breast.[2]
Irregular menstruation.[2]
Vertigo.[2]
3. Blurring of vision.[2] Conjunctivitis.[2]
4. Dampness and swelling of the foot.[2]
5. Malaria.[1] Scrofula.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression distal to the junction of the 4th and 5th
metatarsal
bones, on the lateral side of the tendon of entensor digiti minimi of foot.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
GB 42 Diwuhui *
INDICATIONS
1. Redness an swelling of the dorsum of foot.[1,2]
2. Distending pain of the breast.[1]
Mastitis.[2] Swelling of the axillary
region.[1]
3. Red and painful eyes.[1]
4. Low back pain.[2]
5. Tinnitus.[2]
LOCATION: Between the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones, on the medial
side of the tendon of extensor digiti minimi of foot.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-10 mm.[1]
GB 43 Xiaxi*
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the outer canthus.[1] Blurring
of vision.[1] Pain in the cheek, submandibular
region and costal and hypochondriac region.[1]Migraine.[2]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
2. Tinnitus.[1,2]
3. Hypertension.[2]
4. Febrile diseases.[1]
LOCATION: Between the 4th and 5th toes, proximal to the margin of the
web.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely upward 5-8 mm.[1]
GB 44 Foot-Qiaoyin *
INDICATIONS
1. Migraine.[2] Headache.[2]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2] One-sided
headache.[1]
2. Opthalmalgia.[1] Conjunctivitis.[2]
3. Asthma.[2] Pleurisy.[2]
4. Hypertension.[2]
5. Deafness.[1]
6. Pain in the hypochondriac region.[1]
7. Dream disturbed sleep.[1]
8. Febrile diseases.[1]
LOCATION: On the lateral side of the 4th toe, about 0.1 cun posterior
to the corner of the nail.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 3-5 mm.[1]
[1] Essentials of Chinese Acupuncture Shanghai
[2] Acupuncture A comprehensive Text Beijing